Abstract
Currently, majority of the researchers concentrate on algal biomass production with autotrophic cultivation, however this cultivation strategy induces low biomass yield and it is troublesome to be utilized in large-scale algal biomass production. In contrary to this, heterotrophic algae can accumulate high level lipid production. Therefore, the present study was aimed to assess the effect of various carbon sources viz., glucose, sucrose, fructose, glycerol, sodium acetate and various nitrogen sources viz., NaNO3, urea, KNO3, NH4NO3, yeast extract, peptone, beef extract on lipid, biomass, total chlorophyll, protein and carbohydrate content in Scenedesmsus dimorphus. Among carbon sources, glucose showed maximum biomass yield (1.98±0.005gL-1) and highest lipid content (32.7±0.01%) followed by fructose, sucrose and glycerol. Similarly, total carbohydrates and protein content was also found to be maximum in glucose 0.275±0.002 mgmL-1 and 0.031±0.001 mgmL-1 respectively. While sodium nitrate supported maximum chlorophyll content (29.00±0.01 µgmL-1). Among various tested nitrogen sources, beef extract showed highest lipid production (30.28±0.05%), biomass yield (1.73±0.02 gL-1) in sodium nitrate and total carbohydrates (0.247±0.008) mgmL-1 in beef extract, followed by yeast extract and peptone. Highest chlorophyll content has been found in urea and maximum protein content in ammonium nitrate.
License
This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Article Type: Research Article
EUR J SUSTAIN DEV RES, Volume 2, Issue 4, 2018, Article No: 43
https://doi.org/10.20897/ejosdr/3911
Publication date: 04 Oct 2018
Article Views: 2439
Article Downloads: 2506
Open Access HTML Content References How to cite this articleHTML Content
INTRODUCTION
Being among one of the key biofuels, biodiesel plays a major role in diversifying the supply of world transportation fuels (Yuan et al., 2005; Hansen et al., 2006) . The sustainable and efficient production of biofuel can lead to reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, lowered climate change impact and increased security owing to the fulfilment of global energy demands (González-González et al., 2018). Traditional seed crops comparable to soyabean, rapeseed and palm oil are adopted extensively for biodiesel production. However, to satisfy the increasing demand of biodiesel, seeking lipid-rich biological materials other than traditional oilseed crops has attracted much attention (Shen et al., 2009). Microalgae are considered a potential source of biodiesel because of their relatively simple cellular structure, high lipid content and after the removal of the lipid fraction (Gouveia et al., 2018) the remaining residual biomass (mainly carbohydrates and proteins) can also be used for high value by-products (Pienkos and Darzins, 2009; Bajwa et al., 2017) with additional photosynthetic efficiency (Talebi et al., 2011; González-González et al., 2018). Moreover, some microalgae can be cultivated in non-airable lands using non-potable water or even wastewater, thus reducing or avoiding competition with food/feed crops for agricultural land and freshwater (Chisti et al., 2007; Shen et al., 2008; Shuba and Kifle, 2018). Hundreds of microalgal strains capable of manufacturing high content of lipid are screened and their lipid production metabolisms have been characterized and reported (Sheehan et al., 1998). Many studies have shown that numerous cultivation conditions could increase lipid content in some microalgae equivalent to element deprivation, phosphate, nitrate, high intensity, nutrient media characteristics, low temperature, high salt concentration, and high iron concentration (Illman et al., 2000; Liu et al., 2008). Under these stress conditions, many microalgae respond by significantly increasing lipid content, commonly ranging from 30% to 60% of the dry cell weight. Among these factors, nitrogen is known to have a vigorous effect on the metabolism of lipids and fatty acids in several microalgae (Hsieh et al., 2009; Liang et al., 2009). For biomass production and cellular lipid accumulation, heterotrophic and mixotrophic cultures have been proposed as feasible alternatives (Yu et al., 2009). In comparison to photoautotrophy, heterotrophic cultivation allows higher algal growth rate and enables microalgae to accumulate higher biomass and amounts of lipid using less time in the absence of light, which is critical for reducing the microalgal biomass production cost (Cheirsil et al., 2012). However, only a few microalgae species adapt to heterotrophic cultivation and most of them belong to the genus Chlorella (Isleten-Hosoglu et al., 2012). Heterotrophic growth of microalgae involves the utilization of organic compounds as sole carbon and energy sources. Heterotrophic and mixotrophic cultures of microalgae have been reported using different carbon sources, such as glucose, sucrose, glycerol and sugarcane molasses (Heredia-Arroyo et al., 2011). However, glucose is most commonly used for sustaining microalgae growing in the dark and was used as carbon source in mixotrophic culture of several microalgal species reaching high biomass and lipids productivity (Wan et al., 2011; Xiong et al., 2010; Dittamart et al., 2014).Often carbon and nitrogen are the most important nutrients contributing to the biomass production. Nitrogen in the form of nitrate, ammonia and urea are the most common nitrogen sources. Nitrogen is mostly supplied as nitrate and an increase in pH occurs when nitrate is supplied as the only nitrogen source (Prabakaran Ravindran, 2012) . Chlorella sp. M2 isolate was able to utilize several nitrogen sources including urea, ammonium carbonate, potassium nitrate, ammonium nitrate and sodium nitrate at concentrations ranged from half to 16 folds of recommended concentration in BBM medium (Amin et al., 2013). Urea as a nitrogen source enhanced Chlorella sp. M2 growth more than the other examined nitrogen sources at wide range of concentrations. Carbon and nitrogen source changes will greatly affect the biomass and lipid production of microalgae. Dittamart et al., cultured the Scenedesmus sp. AARL G022 under different organic carbon sources such as glucose, glycerol and sodium acetate and found glucose most suitable for biomass growth (Dittamart et al., 2014). Scenedesmus sp. cultured under three monosaccharides (fructose, maltose, glucose), three organic acids (acetate, propionate, butyrate) and one disaccharide (sucrose) were used to investigate the influence of carbon source on heterotrophic growth and lipid production in dark condition (Hong et al., 2013). The main objective of this work was to investigate the effect of carbon sources and nitrogen sources on total biomass (gL-1) and lipid yield % and other physio-biochemical parameters by the green microalgae Scenedesmus dimorphus.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Isolation and Identification of Isolate
Water samples were collected from Aulakhpur village, Muktsar, (India) and were inoculated in autoclaved BG11 medium at 25±1°C below cool white fluorescent light until algal growth was detected and cultured on BG11 medium enriched agar plates. Individual colonies were picked up and cultured in liquid BG11 medium. The streaking and inoculation procedures were repeated 3-4 times till pure cultures were obtained. The algal cells were observed under microscope for its morphological features and different cellular details. Purified algal species was identified with the help of algal identification guide on the basis of morphological features under the light microscope and more confirmed microalgal species with the assistance of Dr. R. Dhandapani, Department of Microbiology, Periyar University, Salem (Tamil Nadu). Purity of culture were maintained by regular sub culturing similarly microscopic observation under microscope.
Culture Condition and Culture Medium with Nitrogen and Carbon Sources
In autotrophic condition, algal cells in the stationary phase were inoculated into 250 ml Erlenmeyer flasks containing 100 ml BG11 medium, which had been adjusted pH 7 and autoclaved at 121°C for 30 min. The microalgae were cultured at 25±1°C using BOD incubator cum shaker at 120 rpm having florescence light of around 3000 lux. For heterotrophic culture, the selection of carbon sources to enhance the growth of algae was carried out directly in BG-11 media amended with 1% (w/v) of six various organic carbon sources (fructose, glucose, fructose, sucrose sodium acetate, glycerol. The experiments was conducted in triplicate along with control parallel run in which no additional carbon sources were added. Beef extract, urea, peptone, ammonium nitrate, sodium nitrate, potassium nitrate and yeast extract were chosen as the nitrogen sources with the initial concentrations computed as the same nitrogen atom number of sodium nitrate. All the biochemical and physiological parameters such as total biomass, lipid, total chlorophyll, carbohydrates and protein were analyzed after a cultivation period of 12 days.
Estimation of Cellular Components
Bligh and Dyer Lipid Extraction Method
Total lipids were extracted by mixing methanol-chloroform (2:1.5 v/v) with the algal samples using slightly modified version of Bligh and Dyer’s method (Bligh and Dyer, 1959). Algal biomass pellet was collected by centrifuging 50 mL of the algal culture at 5,000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was discarded and the algal biomass was incubated for 24 h at 25°C in a mixture of 2 mL methanol and 1.5 mL chloroform. The mixture was then vortexed for 2 min, followed by the addition of 1.5 mL of chloroform and agitation again for 1 min. The mixture was amended with 1.8 mL distilled water followed by 2 min of vigorous agitation. It was then centrifuged for 10 min at 2,000 rpm and a lower lipid layer was separated carefully using Eppendroff micropipettes in a clean previously dried (104°C) and preweighed 15-mL glass centrifuge tube. The chloroform phase was evaporated near to dryness in a water bath at 70°C, and the residue was dried further at 104°C for 30 min. Lipid content was described as percentage dcw (Bligh and Dyer, 1959).
Estimation of Dry Biomass
Dry cell biomass was measured as the cell density (dcw, gL-1) at OD 625 of an 11-day-old culture at dilutions ranging from 0.2 to 1.0. The dry biomass was calculated using the regression equation relationship given by Yount (Yount, 2006) , y = 0.1015x + 0.2071 , R² = 0.9456
Extraction and Determination of Photosynthetic Pigment (Chlorophyll)
A known volume of algal cultures was centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 10 min and rinsed twice with distilled water. The pellet was extracted twice with 95 % methanol, followed by centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 10 min. The contents of total chlorophyll in the supernatant were determined by UV-VIS spectroscopy. Chlorophyll content of the algae was estimated spectrophotometrically at 650 and 665 nm (Mackinney, 1941).The concentration of chlorophyll was calculated using the formula:
Total chlorophyll (mgmL-1) = 2.55 × 10-2 E650 + 0.4 × 10-2 E665 × 103
Extraction and Determination of Total Soluble Carbohydrates
A known volume of algal cells were centrifuged, discharged supernatant. Algal biomass was hydrolyzed with 2.5 N HCl for 3 hours in water bath. After complete hydrolysis, again centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 5 mins. Briefly 0.5 ml of hydrolyzed algal sample mixed with distilled water to make a final volume 1 ml and added 4 ml of Anthrone reagent into homogenized mixture, incubated in boiling water bath for 10 min. Carbohydrate was determined at 625 nm by Anthrone reagent method (Dubois et al.,1956). Standard curve prepared by using graded conc. of glucose dilution ranging from 0.2 to 1.
y = 0.636x + 0.0592, R² = 0.9987
Total Protein Estimation
-
Bovine serum albumin (BSA) stock solution (1mgmL-1),
-
Analytical reagents:
-
50 ml of 2% sodium carbonate mixed with 50 ml of 0.1 N NaOH solution (0.4 gm in 100 ml distilled water.
-
10 ml of 1.56% copper sulphate solution mixed with 10 ml of 2.37% Sodium potassium tartarate solution.
-
Prepared analytical reagents by mixing 2 ml of (b) with 100 ml of (a)
-
Folin - Ciocalteau reagent solution (1N) dilute commercial reagent (2N) with an equal volume of water on the day of use (2 ml of commercial reagent + 2 ml distilled water). This solution is incubated at room temperature for 10 mins.
Procedure
10 ml of homogenized algal suspension was taken in 10 ml centrifuge tube and centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 5 minutes. Discard the supernatant, added 0.1 N NaOH to the pellet and incubated in water bath at 60oC for 30 minutes to hydrolyze the pellet and centrifuged again. Briefly taken 0.5 ml hydrolyzed sample, 0.5 mL of reagent (A) was added. The tubes were then heated in a boiling water bath for 10 min and cooled in running tap water. Subsequently, 2.5 mL of reagent (B) was added in each and the tubes were incubated at room temperature for 10 mins. After this, 0.5 mL of reagent (C) was added. The tubes were kept at room temperature for 15 mins. The intensity of blue colour was read as absorbance at 660 nm against appropriate blank. The protein content was estimated using a standard calibration curve prepared from bovine serum albumin and expressed in terms of mgmL-1. Protein concentration was calculated from the standard curve prepared with bovine serum albumin (BSA). y = 0.1097x - 0.0005, R² = 0.9989 (Lowry et al., 1951)
Statistical Analysis
Statistical comparison between the groups was done by multi factor one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s multiple-range test, using SPSS version 21.0. The p-values that were less than 0.05 were considered significant.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In the present investigation, fresh water green microalga has been isolated from enriched mixed culture by standard isolation technique. Further cellular characteristics and morphological features of the isolate have demonstrated its close similarity with genus Scenedesmus dimorphus and also observed under fluorescent microscope for lipid detection (Figure 1 A, B). In Scenedesmus dimorphorus, neutral lipid or triglycerides appeared as yellow dots, whereas polar lipid and chlorophyll stained in red colour cells by Nile Red staining under fluorescent microscope with excitation wavelength at 420 nm and emission at 580-nm. Similar finding have been reported by many workers for lipid staining by using Nile Red dye for intracellular lipid identification (Cooksey et al., 1987; Matsunaga et al., 2009; Elumalai et al., 2011; Abdo et al., 2014; Kirrolia, 2015; Kiran et al., 2016).
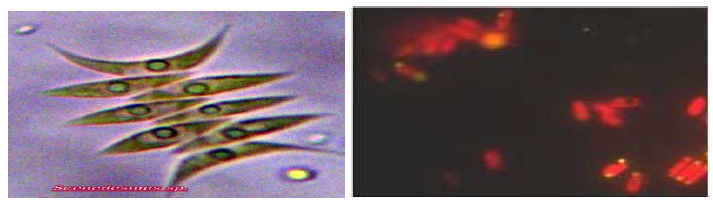
In the present study, effect of various nitrogen and carbon sources were investigated on total lipid content, biomass, chlorophyll, cellular protein and carbohydrate contents. Scenedesmus sp. was grown in BG-11 for 14 days and source of nitrogen sodium nitrate is replaced by KNO3, urea, peptone, beef, ammonium nitrate with parallel running control.
The effect of different carbon sources on biomass (g L-1), lipid (% dcw ), total chlorophyll (µg mL-1), protein (mgmL-1) and total carbohydrate mgmL-1 of Scenedesmus sp. is shown in Table 1 and Figure 2. Biomass yield was found to be significantly higher (P≤0.05) when Scenedesmus sp. cultured with glucose amended BG-11 media , followed by sucrose. Glucose and fructose is easily taken up by microbial cells, disaccharides like sucrose or lactose must be first hydrolyzed to monosaccharides or must have specific transport system before entering microbial cells as advocated by Perez-Garcia et al., 2011. Lipid content was also found to be significant higher (P≤0.05) in glucose followed fructose as shown in Table 1, Figure 2. According to Ren et al., (2013) maximum biomass yield and lipid production have been reported in new lipid rich microalgae Scenedesmus sp. strain R-16 and observed that glucose was found to be efficient carbon source for maximum biomass yield (3.46 g L-1) lipid content (43%) and specific growth rate (0.819 d-1). Sharma et al., (2015) observed that among organic carbon sources, the maximum lipid content (13.22% and lipid yield 189.94 mgL-1, biomass yield 1.43±0.075gL-1 and lipid productivity 86.04±3.2 mgL-1d-1 were found in case of glucose, followed by glycerol and sucrose. The present results are also supported by Griffiths et al., (1960) and observed that higher growth rate has found in glucose among various sugars such as organic acids, phosphate of sugars and monohydric alcohols. Present results are in agreement with the finding of Kirrolia et al., 2013.They reported a biomass yield 1.66 gL-1 and lipid content 16.52±0.25 at 1% glucose concentration supplementation for Chlorella species (Kirrolia et al., 2013).This difference might be due to the species difference.
|
Table 1. Effect of carbon sources on physio-chemical components of Scenedesmus dimorphus
a, b, c, d, e Means with unlike superscript in the column differ significantly (P≤0.05) |
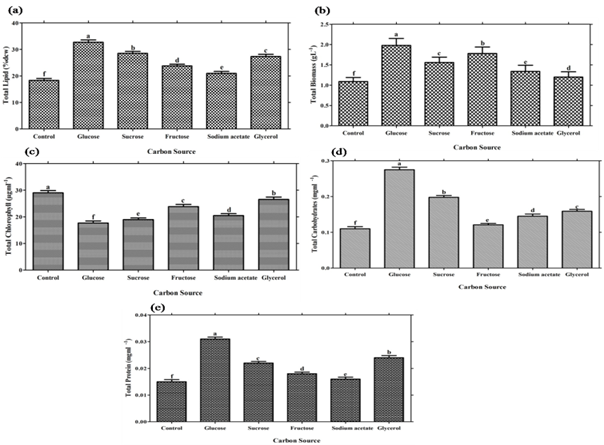
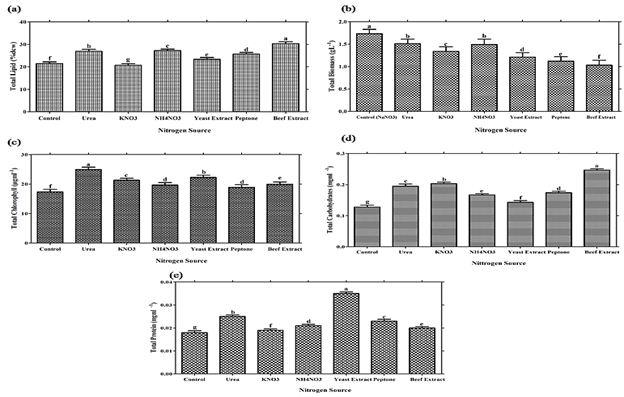
According to Dittamart et al., (2014), Scenedesmus sp. AARL G022 under different organic carbon sources such as glucose, glycerol and sodium acetate and found glucose most suitable for biomass growth. Hong et al., (2013) reported that Scenedesmus sp. cultured under three monosaccharides (fructose, maltose, glucose), three organic acids (acetate, propionate, butyrate) and one disaccharide (sucrose) were used to investigate the influence of carbon source on heterotrophic growth and lipid production in dark condition and found glucose most suitable for lipid production.Interestingly, Scenedesmus sp. showed significant (P≤0.05) total chlorophyll production (Table 1, Figure 2 C). While significant (P≤0.05) results of total protein and carbohydrates were reported in glucose as compared with other carbon sources (Table 1, Figure 2 D, E). Nitrogen is an important constituent of cell protein and protoplasm needed for algal growth and it affects the productivity of microalgae. Microalgae are capable of utilizing various dissolved forms of inorganic and organic nitrogenous sources. An essential criterion for mass production of microalgae varies from species to species; it is based on the selection and utilization of a suitable nitrogen source (Tape et al., 2006). In addition, Scenedesmus sp. can utilize both inorganic and organic nitrogen sources for growth and lipid accumulation but organic nitrogen sources has much significant effects for lipid production in comparison with inorganic nitrogen source. Among various nitrogen sources, Scenedesmus sp. showed significant (P≤0.05) biomass yield for sodium nitrate and lipid % dcw for beef extract. (Table 2, Figure 3). Maximum lipid content achieved i.e. 30.28 % when Scenedemus sp. cultured with media having beef extract as a nitrogen source followed by yeast extract and peptone. It might be reason for inefficient utilization of beef extract could result in the N-starvation of algal cells which induced higher total lipid content of algae (Wan et al., 2012). Moreover, growth data suggest that nitrogen source preference might vary between the algal species (Xiong et al., 2008; Shen et al., 2010). In present study, it has been found that urea has led to significant chlorophyll production in comparison with other nitrogen source (Table 2, Figure 3,C). Pandian and Ravindran (2012) have found that Chlorococcum treated with different nitrogen sources showed maximum amount of chlorophyll content in 0.02% of urea (Pandian and David, 2012). Urea seems to be the most effective nitrogen source for providing the alga with sufficient carbon and at the same time nitrogen comparable to a nitrate source (El-shayed et al., 2011). Agwa and his co-worker stated that urea is found most appropriate nitrogen source for overall growth of Chlorella vulgaris (Agwa and Abu, 2016). Significant carbohydrates (P≤0.05) concentration have been found in beef extract. It is also reported that certain concentration of urea could stimulate the accumulation of photosynthetic pigments and intensify photosynthesis in Elodea densa (Maleva et al., 2015). However the protein concentration was found to be significant (P≤0.05) in yeast extract as comparison was made with other nitrogen source.
|
Table 2. Effect of nitrogen sources on physio-chemical components of Scenedesmus dimorphus
a, b, c, d, e, f, g Means with unlike superscript in the column differ significantly (P≤0.05) |
CONCLUSION
Both the nitrogen and carbon source had substantial effect on lipid productivity, biomass yield and physico-biochemical composition of Scenedesmus dimorphus. Among various carbon sources, organic carbon sources have much significant effects. Glucose had led to maximum lipid content 32.7% and biomass yield 1.98 gL-1. Scenedesmus sp. showed significant total chlorophyll content for sodium nitrate followed by sodium acetate and least for glucose. Among various tested nitrogen sources, beef extract showed significantly enhanced lipid production i.e. 30.28%, while biomass yield have been found maximum in sodium nitrate. In the case of total chlorophyll urea showed much significant effects. However, highest carbohydrate content in Scenedesmus sp. has been reported with beef extract and maximum cellular protein content in ammonium nitrate. Therefore beef extract and glucose has much significant effects on lipid content and biomass yield.Hence heterotrophic cultivation can be suitable alternative for maximum biomass and lipid production.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are grateful to Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, Guru Jambheshwar university of Science and Technology, Hisar (Haryana) for providing necessary facilities during the research work. We also gratefully thank to Dr. R. Dhandapani, Department of Microbiology, Periyar University, Salem (Tamil Nadu) India for providing the necessary help for identification of microalgal species. This financial support was provided by the University Grant Commission under Maulana Azad National Fellowship for Minorities (MANF).
References
- Abdo, S. M., Ahmed, E., El-Enin, S. A., El Din, R. S. and Ali, G. E. D. G. (2014). Qualitative and quantitative determination of lipid content in microalgae for biofuel production. J. Algal Biomass Utln., 5(3), 23-28.
- Agwa, O. K. and Abu, G. O. (2016). Influence of Various Nitrogen Sources on Biomass and Lipid Production by Chlorella vulgaris. British Biotechnology Journal, 15(2), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.9734/BBJ/2016/21727
- Amin, N. F., Khalafallah, M. A., Ali, M. A., Abou-Sdera, S. A. and Matter, I. A. (2013). Effect of some nitrogen sources on growth and lipid of microalgae Chlorella sp. for biodiesel production. Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 9(8), 4845-4855.
- Bajwa, K., Bishnoi. N. R., Kirrolia, A., Sharma, J., Gupta, S (2017). Comparison of various growth media composition for physio-biochemical parameters of biodiesel producing microalgal species (Chlorococcum aquaticum, Scenedesmus obliquus, Nannochloropsis oculata and Chlorella pyrenoidosa). European Journal of Biotechnology and Bioscience, 5(6), 27-31.
- Bligh, E. G., and Dyer, W. J. (1959). A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Canadian journal of biochemistry and physiology, 37(8), 911-917. https://doi.org/10.1139/o59-099
- Chisti, Y. (2007). Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol Adv, 25, 294-304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2007.02.001
- Cooksey, K. E., Guckert, J. B., Williams, S. A. and Callis, P. R. (1987). Fluorometric determination of the neutral lipid content of microalgal cells using Nile Red. Journal of microbiological methods, 6(6), 333-345. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-7012(87)90019-4
- Dittamart, D., Pumas, C., Pekkoh, J., and Peerapornpisal, Y. (2014). Effects of organic carbon source and light-dark period on growth and lipid accumulation of Scenedesmus sp. AARL G022. Maejo International Journal of Science and Technology, 8(2), 198-206.
- Dubois, M., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Rebers, P. A. T. and Smith, F. (1956). Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Analytical chemistry, 28(3), 350-356. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60111a017
- Elumalai, S., Prakasam, V. and Selvarajan, R. (2011). Optimization of abiotic conditions suitable for the production of biodiesel from Chlorella vulgaris. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 4(2), 91-97.
- González-González, L. M., Correa, D. F., Ryan, S., Jensen, P. D., Pratt, S. and Schenk, P. M. (2018). Integrated biodiesel and biogas production from microalgae: Towards a sustainable closed loop through nutrient recycling. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 82, 1137-1148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.09.091
- Gouveia, L., Oliveira, A. C., Congestri, R., Bruno, L., Soares, A. T., Menezes, R. S. and Tzovenis, I. (2018). Biodiesel from microalgae. In Microalgae-Based Biofuels and Bioproducts (pp. 235-258).
- Griffiths, D. J., Thresher, C. L., and Street, H. E. (1960). The heterotrophic nutrition of Chlorella vulgaris (Brannon No. 1 strain): with two figures in the text. Annals of Botany, 24(1), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aob.a083682
- Hansen, A. C., Gratton, M. R. and Yuan, W. (2006). Diesel engine performance and NOx emissions from oxygenated biofuels and blends with diesel fuel. Transactions of the ASABE, 49(3), 589-595. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.20475
- Heredia-Arroyo, T., Wei, W., Ruan, R., and Hu, B. (2011). Mixotrophic cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris and its potential application for the oil accumulation from non-sugar materials. Biomass Bioenergy, 35, 2245– 2253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2011.02.036
- Hsieh, C. H. and Wu, W. T. (2009). Cultivation of microalgae for oil production with a cultivation strategy of urea limitation. Bioresource technology, 100(17), 3921-3926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.03.019
- Illman, A. M., Scragg, A. H. and Shales, S. W. (2000). Increase in Chlorella strains calorific values when grown in low nitrogen medium. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 27(8), 631-635. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(00)00266-0
- Isleten-Hosoglu, M., Gultepe, I. and Elibol, M. (2012). Optimization of carbon and nitrogen sources for biomass and lipid production by Chlorella saccharophila under heterotrophic conditions and development of Nile red fluorescence based method for quantification of its neutral lipid content. Biochemical engineering journal, 61, 11-19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2011.12.001
- Kiran, B., Pathak, K., Kumar, R., Deshmukh, D. and Rani, N. (2016). Influence of varying nitrogen levels on lipid accumulation in Chlorella sp. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 13(7), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1021-4
- Kirrolia, A., Bishnoi, N. R. and Singh, R. (2013). Microalgae as a boon for sustainable energy production and its future research and development aspects. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 20, 642-656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.12.003
- Kirrolia. A, (2015). A study on biodiesel production from microalgae Ph.D thesis. Guru Jambheshwar University of Science & Technology, Hisar (Haryana).
- Liang, Y., Sarkany, N. and Cui, Y. (2009). Biomass and lipid productivities of Chlorella vulgaris under autotrophic, heterotrophic and mixotrophic growth conditions. Biotechnology letters, 31(7), 1043-1049. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-9975-7
- Liu, Z. Y., Wang, G. C. and Zhou, B. C. (2008). Effect of iron on growth and lipid accumulation in Chlorella vulgaris. Bioresource technology, 99(11), 4717-4722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.09.073
- Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L. and Randall, R. J. (1951). Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J biol Chem, 193(1), 265-2.
- Mackinney, G. (1941). Absorption of light by chlorophyll solutions. J. biol. Chem, 140(2), 315-322.
- Maleva, M., Borisova, G., Chukina, N. and Prasad, M. N. V. (2015). Urea-induced oxidative damage in Elodea densa leaves. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(17), 13556-13563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4600-x
- Matsunaga, T., Matsumoto, M., Maeda, Y., Sugiyama, H., Sato, R. and Tanaka, T. (2009). Characterization of marine microalga, Scenedesmus sp. strain JPCC GA0024 toward biofuel production. Biotechnology Letters, 31(9), 1367-1372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0029-y
- Pandian, P. and David, A., and Ravindran. (2012). Influence of different Carbon and Nitrogen sources on growth and CO2 fixation of microalgae. Advances in Applied Science Research, 3(3),1714-1717.
- Perez-Garcia, O., Escalante, F. M., de-Bashan, L. E. and Bashan, Y. (2011). Heterotrophic cultures of microalgae: Metabolism and potential products. Water Research, 45(1), 11-36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.08.037
- Pienkos, P. T. and Darzins, A. L. (2009). The promise and challenges of microalgal derived biofuels. Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, 3(4), 431-440. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.159
- Ren, H. Y., Liu, B. F., Ma, C., Zhao, L. and Ren, N. Q. (2013). A new lipid-rich microalga Scenedesmus sp. strain R-16 isolated using Nile red staining: effects of carbon and nitrogen sources and initial pH on the biomass and lipid production. Biotechnology for biofuels, 6(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-6-143
- Sharma, A. K., Sahoo, P. K. and Singhal, S.(2015). Screening and optimization of culture media for Chlorella sp. as a raw material for biodiesel production. Int J pharma bio sci., 6(3), 251- 262.
- Shen, Y., Yuan, W., Pei, Z. J., Wu, Q. and Mao, E. (2009). Microalgae mass production methods. Transactions of the ASABE, 52(4), 1275-1287. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.27771
- Shen, Y., Yuan, W., Pei, Z. and Mao, E. (2008). Culture of microalga Botryococcus in livestock wastewater. Transactions of the ASABE, 51(4), 1395-1400. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.25223
- Shen, Y., Yuan, W., Pei, Z. and Mao, E. (2010). Heterotrophic culture of Chlorella protothecoides in various nitrogen sources for lipid production. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 160(6), 1674-1684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8659-z
- Shuba, E. S. and Kifle, D. (2018). Microalgae to biofuels: Promising alternative and renewable energy, review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 81, 743-755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.08.042
- Talebi, A. F., Mohtashami, S. K., Tabatabaei, M., Tohidfar, M., Bagheri, A., Zeinalabedini, M. and Bakhtiari, S. (2013). Fatty acids profiling: a selective criterion for screening microalgae strains for biodiesel production. Algal Research, 2(3), 258-267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2013.04.003
- Tepe, Y., Naz, M. and Türkmen, M. (2006). Utilization of different nitrogen sources by cultures of Scenedesmus acuminatus. 6,123-127.
- Wan, M. X., Wang, R. M., Xia, J. L., Rosenberg, J. N., Nie, Z. Y., Kobayashi, N. and Betenbaugh, M. J. (2012). Physiological evaluation of a new Chlorella sorokiniana isolate for its biomass production and lipid accumulation in photoautotrophic and heterotrophic cultures. Biotechnology and bioengineering, 109(8), 1958-1964. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24477
- Wan, M., Liu, P., Xia, J., Rosenberg, J. N., Oyler, G. A., Betenbaugh, M. J. and Qiu, G. (2011). The effect of mixotrophy on microalgal growth, lipid content, and expression levels of three pathway genes in Chlorella sorokiniana. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 91(3), 835-844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3399-8
- Xiong, W., Gao, C., Yan, D., Wu, C. and Wu, Q. (2010). Double CO2 fixation in photosynthesis–fermentation model enhances algal lipid synthesis for biodiesel production. Bioresource Technology, 101(7), 2287-2293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.11.041
- Yount, R. (2006). Advanced statistical procedures, research design and statistical analysis in Christian Ministry. Southwestern Baptist Theological Seminary, Fort Worth.
- Yu, H., Jia, S. and Dai, Y. (2009). Growth characteristics of the cyanobacterium Nostoc flagelliforme in photoautotrophic, mixotrophic and heterotrophic cultivation. Journal of Applied Phycology, 21(1), 127-133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-008-9341-5
- Yuan, W., Hansen, A. C., Tat, M. E., Van Gerpen, J. H. and Tan, Z. (2005). Spray, ignition, and combustion modeling of biodiesel fuels for investigating NOx emissions. Transactions of the ASAE, 48(3), 933-939. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.18498
How to cite this article
APA
Bajwa, K., Bishnoi, N. R., Kirrollia, A., & Selvan, S. T. (2018). A New Lipid Rich Microalgal SP Scenedesmus Dimorphus Isolated: Nile Red Staining and Effect of Carbon, Nitrogen Sources on its Physio-Biochemical Components. European Journal of Sustainable Development Research, 2(4), 43. https://doi.org/10.20897/ejosdr/3911
Vancouver
Bajwa K, Bishnoi NR, Kirrollia A, Selvan ST. A New Lipid Rich Microalgal SP Scenedesmus Dimorphus Isolated: Nile Red Staining and Effect of Carbon, Nitrogen Sources on its Physio-Biochemical Components. EUR J SUSTAIN DEV RES. 2018;2(4):43. https://doi.org/10.20897/ejosdr/3911
AMA
Bajwa K, Bishnoi NR, Kirrollia A, Selvan ST. A New Lipid Rich Microalgal SP Scenedesmus Dimorphus Isolated: Nile Red Staining and Effect of Carbon, Nitrogen Sources on its Physio-Biochemical Components. EUR J SUSTAIN DEV RES. 2018;2(4), 43. https://doi.org/10.20897/ejosdr/3911
Chicago
Bajwa, Kulvinder, Narsi R. Bishnoi, Anita Kirrollia, and Silambarasan Tamil Selvan. "A New Lipid Rich Microalgal SP Scenedesmus Dimorphus Isolated: Nile Red Staining and Effect of Carbon, Nitrogen Sources on its Physio-Biochemical Components". European Journal of Sustainable Development Research 2018 2 no. 4 (2018): 43. https://doi.org/10.20897/ejosdr/3911
Harvard
Bajwa, K., Bishnoi, N. R., Kirrollia, A., and Selvan, S. T. (2018). A New Lipid Rich Microalgal SP Scenedesmus Dimorphus Isolated: Nile Red Staining and Effect of Carbon, Nitrogen Sources on its Physio-Biochemical Components. European Journal of Sustainable Development Research, 2(4), 43. https://doi.org/10.20897/ejosdr/3911
MLA
Bajwa, Kulvinder et al. "A New Lipid Rich Microalgal SP Scenedesmus Dimorphus Isolated: Nile Red Staining and Effect of Carbon, Nitrogen Sources on its Physio-Biochemical Components". European Journal of Sustainable Development Research, vol. 2, no. 4, 2018, 43. https://doi.org/10.20897/ejosdr/3911

 Full Text (PDF)
Full Text (PDF)